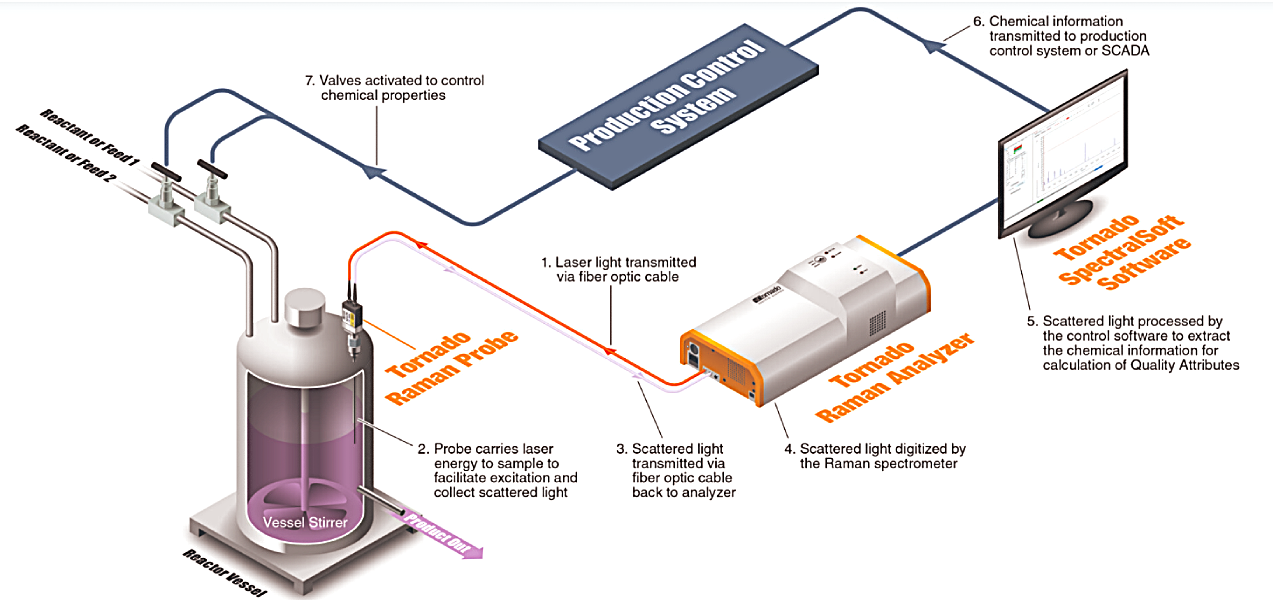
BIOPROCESS MONITORING
Raman spectroscopy is a recognized PAT (Process Analytical Tool) that has been seen as a central spectroscopic tool used in bioprocessing. It plays a pivotal role in the monitoring of fermentations, particularly their optimization within the PAT framework and harnesses biological processes for the development of drug therapies, providing treatments that range from small molecule antibiotics to large recombinant proteins.